Using an EDTA tube correctly is essential for reliable blood sample collection, preservation, and laboratory testing. EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) tubes are widely used in clinical and diagnostic settings because EDTA acts as an anticoagulant, preventing blood clotting and preserving cellular components for analysis. This detailed guide covers everything you need to know about how to use an EDTA tube, including its composition, types, handling, and applications.
What is an EDTA Tube and Why Is It Important?
An EDTA tube is a specialized blood collection tube coated or containing EDTA powder. The EDTA binds calcium ions in the blood, inhibiting clot formation and keeping the blood in a fluid state. This characteristic is crucial for tests that require whole blood or plasma without clot interference.
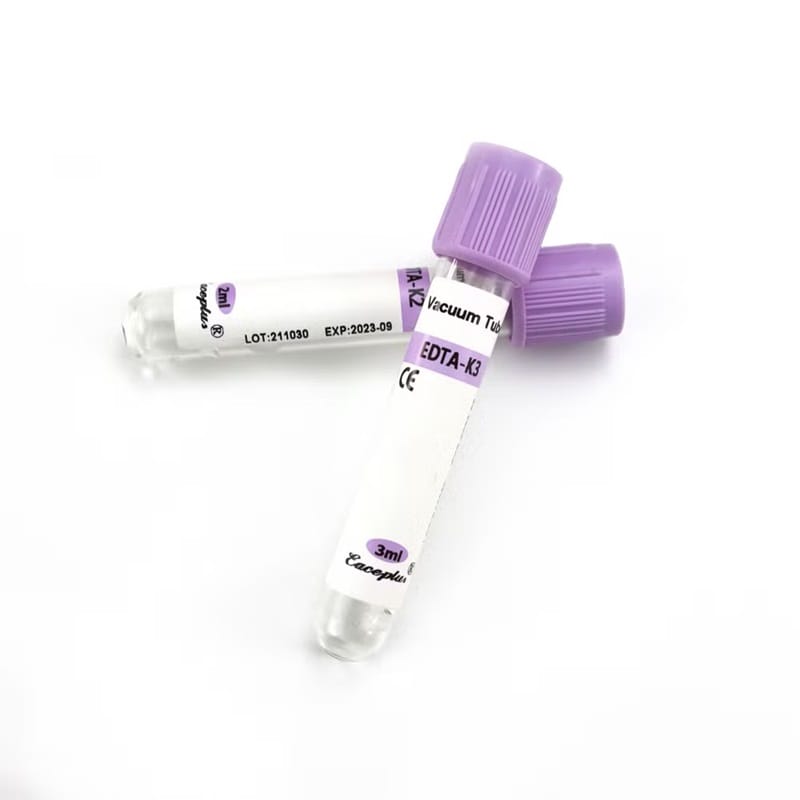
EDTA tubes are commonly used for hematology tests such as complete blood counts (CBC), platelet counts, and blood smears.
For more details, visit What is an EDTA Tube and How Do I Use It?.
Composition and Types of EDTA Tubes
Understanding the material and types of EDTA tubes helps ensure proper selection for your testing needs.
Materials Used: EDTA tubes are typically made from high-quality medical-grade plastic or glass. The anticoagulant (EDTA) is coated inside or added in powdered form. Learn more about tube materials here.
Types of EDTA Tubes:
K2 EDTA Tubes: Contain spray-coated dipotassium EDTA, preferred for flow cytometry and molecular diagnostics.
K3 EDTA Tubes: Contain liquid tripotassium EDTA, suitable for routine hematology tests.
Check detailed uses of K2 and K3 tubes here: EDTA K2 & K3 Tube Whole Blood Tube Uses.
How Does EDTA Work in Blood Collection Tubes?
EDTA works by chelating calcium ions, a vital component in the blood coagulation pathway. By sequestering calcium, EDTA effectively prevents the coagulation cascade from progressing, preserving the blood cells and plasma in their native state.
This anticoagulant mechanism makes EDTA tubes ideal for accurate hematological measurement where cell morphology and counts must remain intact.
For a detailed scientific explanation visit: How Does EDTA Work?.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an EDTA Tube
Using an EDTA tube correctly involves specific procedures to ensure sample integrity and accurate test results.
1. Preparation Before Collection
Always confirm patient identity.
Gather all necessary equipment: EDTA tubes, needles, tourniquet, alcohol swabs, gloves, and sharps container.
Use tubes from a reliable supplier such as EDTATube.com.
2. Blood Collection Procedure
Apply the tourniquet 3-4 inches above the venipuncture site to engorge the vein.
Clean the repository with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
Insert the needle smoothly into the vein, using standard phlebotomy technique.
Once blood starts flowing, insert the EDTA tube into the holder for automatic filling.
3. Filling the Tube
EDTA tubes are vacuum-sealed; they fill automatically to the marked volume.
Do not overfill or underfill; proper volume ensures correct blood-to-anticoagulant ratio.
Gently invert the tube 8 to 10 times immediately after collection to mix blood with EDTA and prevent clot formation.
4. Handling and Storage
Label the tube accurately with patient information and collection time.
Store the sample at room temperature if testing will be done within 6 hours; refrigeration might be necessary for longer periods.
Avoid vigorous shaking that can cause hemolysis.
Applications of EDTA Tubes in Medical Testing
EDTA tubes serve various clinical purposes, especially in hematology and molecular diagnostics.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets.
Blood Smears: Preserves cellular integrity for microscopic examination.
Molecular Tests: K2 EDTA tubes are preferred for DNA and RNA extraction to prevent coagulation without damaging nucleic acids.
Flow Cytometry: Analysis of cellular markers is facilitated by EDTA tubes due to excellent preservation of cell morphology.
The versatility of EDTA tubes makes them a standard choice in many labs. For product options and detailed medical uses, explore EDTA Tubes for Blood Collection.
Best Practices and Precautions While Using EDTA Tubes
Proper usage is critical for reliable lab results.
Avoid Contamination: Use sterile techniques to prevent bacterial or other contaminations during collection.
Correct Tube Selection: Choose the right volume and anticoagulant type according to test requirements.
Do Not Mix with Other Additives: Avoid mixing EDTA blood with other anticoagulants as it may alter results.
Timely Processing: Analyze samples within recommended timeframes to prevent degradation.
Additional guidelines and quality standards can be found at EDTATube.com About Us.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with EDTA Tubes
Understanding common problems can help maintain sample integrity.
Clotted Samples: Usually caused by insufficient mixing or delayed inversion after collection.
Hemolysis: Aggressive shaking or improper collection technique may lead to red cell rupture.
Underfilled Tubes: Can cause inaccurate anticoagulant concentrations, leading to unreliable test results.
Tube Expiry and Storage: Use tubes before expiration date and store as recommended for optimal performance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations in Using EDTA Tubes
Proper disposal of used EDTA tubes is important to prevent biohazard risks.
Use puncture-resistant sharps containers for disposal.
Follow facility protocols for biohazard waste management.
EDTA itself is generally safe in tubes but should not be ingested or handled improperly.
Further contact information for specialized support can be found here: Contact Us.
Summary
EDTA tube correctly is vital for accurate hematological and molecular diagnostics. Proper understanding of the tube’s composition, anticoagulant mechanism, and best practices for blood collection ensures sample integrity and reliable test outcomes. Always follow meticulous collection protocols, choose the appropriate EDTA tube type, and process samples timely. For quality EDTA tubes and detailed resources, visit EDTATube.com. Staying informed and adhering to clinical standards guarantees effective blood analysis and patient care.
For further insights and updates, check out the Siny Medical YouTube Channel and Siny Medical Marketplace.
FAQs
What is the difference between K2 and K3 EDTA tubes?
K2 EDTA tubes contain spray-coated dipotassium EDTA, best suited for flow cytometry and molecular diagnostics, while K3 EDTA tubes contain liquid tripotassium EDTA, commonly used for routine hematology tests.
How soon should blood in an EDTA tube be tested?
Samples should be analyzed ideally within 6 hours at room temperature; refrigeration can extend stability but should be done cautiously.
Can EDTA tubes be used for coagulation studies?
No, EDTA tubes are not suitable for coagulation studies. Citrate tubes are preferred for coagulation tests.
How many times should I invert the EDTA tube after collection?
Invert gently 8 to 10 times immediately to ensure mixing and prevent clot formation.
Where can I buy quality EDTA tubes?
Reliable suppliers like EDTATube.com and SinyMedical provide medical-grade EDTA tubes.