In clinical diagnostics, the smallest error in how you handle blood collection supplies can lead to inaccurate lab results, wasted time, and the need for a painful redraw. For professionals managing high-volume diagnostics, the integrity of every single sample matters for patient care and operational efficiency. Getting reliable results starts long before the venipuncture—it begins with the proper handling and storage of your supplies. Specifically, how you store and use EDTA Blood Collection Tubes is critical to their performance.
These purple-top tubes contain an essential anticoagulant (often K2 or K3 EDTA Tube) that prevents blood from clotting, making them indispensable for hematology tests like Complete Blood Counts (CBCs). If these tubes are compromised by temperature, expiration, or improper mixing, the EDTA cannot do its job properly. This means the blood sample is unusable, directly affecting diagnostic quality.
This detailed guide will walk you through the non-negotiable best practices for storing, handling, and using your EDTA Tubes. By implementing these steps, you ensure the quality of every sample processed in your facility, maintain compliance, and boost confidence in your diagnostic results. As a trusted global supplier since 2003, we understand that quality assurance is a partnership, and proper technique is everything.
The Foundation of Quality: Optimal Storage Conditions for EDTA Blood Collection Tubes
Proper storage is the first line of defense against compromised samples. Exposure to the wrong conditions can directly affect the anticoagulant’s effectiveness, leading to issues like platelet clumping or hemolysis, which ruins the sample.
Key Factors in Long-Term EDTA Tube Storage
The primary enemy of any vacuum blood collection tube is environmental fluctuation.
Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
All EDTA Blood Collection Tubes are designed to be stable at a specific temperature range.
- Avoid Heat: Excessive heat can damage the plastic components, the rubber stopper, and, most importantly, the anticoagulant coating. High temperatures can cause the vacuum to degrade prematurely, which means the tube won’t draw the correct volume of blood (underfilling), leading to an incorrect blood-to-anticoagulant ratio. This incorrect ratio is one of the fastest ways to generate an unusable specimen.
- Avoid Cold: While freezing is rare, extreme cold can also damage the tube integrity. The tube should never be used if it has been frozen and thawed, as this can cause condensation on the inner walls, diluting the sample or affecting the stability of the additive.
Managing Humidity and Light
Humidity is a subtle threat. High moisture can lead to condensation inside the packaging or even subtly affect the tube’s cap seal over time.
- Dry Environment: Store tubes in a dry area. Keep them in their original packaging until they are ready to be placed in the phlebotomy collection area.
- Keep Out of Direct Light: Direct sunlight or strong UV light can also degrade the components of the tube, even the additives. Always store boxes away from windows or direct, intense light sources.
Original Packaging Protection
The manufacturer’s packaging is designed to protect the tube’s vacuum and sterility.
- Keep Boxes Sealed: Do not open an inner carton until those tubes are needed for use. Once a carton is opened, tubes are more susceptible to dust, humidity, and physical damage.
- Check Integrity: Before moving tubes to a workstation, visually inspect the box for damage, punctures, or signs of moisture that could indicate compromised vacuum or sterility.
A Matter of Accuracy
The expiration date on a box of EDTA Blood Collection Tubes is not a suggestion; it is a hard deadline. Using an expired tube is one of the most common, yet avoidable, pre-analytic errors.
Why Expiration Dates Matter
The date on the box indicates the lifespan of the tube’s most critical elements:
- Vacuum Integrity: Over time, the seal that maintains the vacuum inside the tube can weaken. An expired tube is likely to have a partial or complete loss of vacuum. If the vacuum is low, the tube will underfill, resulting in a critically low blood-to-anticoagulant ratio.
- Anticoagulant Efficacy: While EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is stable, its effectiveness and distribution within the tube can slightly degrade over years, especially if storage conditions have been less than ideal.
Using an underfilled tube from an expired batch can cause the sample to clot partially, or it can lead to cell morphology changes—like red blood cell shrinkage—that make the sample inaccurate for CBC and other hematology tests.
Implementing a FIFO Inventory System
The “First-In, First-Out” (FIFO) system is the gold standard for managing any medical consumable, especially blood collection tubes.7
- New Stock Behind Old: When new inventory of EDTA Tubes arrives, it should always be placed behind the existing stock on the shelves.
- Visible Dates: Ensure that the expiration dates of the oldest stock are clearly visible to phlebotomy staff and procurement.
- Routine Audits: A designated staff member should routinely check the inventory, perhaps weekly or bi-weekly, to pull any tubes approaching their expiration date. They should be removed from the active collection area at least 30 days before expiration.
| Stock Action | Goal | Why It’s Critical |
| Store FIFO | Use oldest stock first | Prevents unnecessary product waste due to expiration. |
| Check Expiration | Verify date before use | Avoids pre-analytic errors from compromised vacuum or additive. |
| Use Tubes at $20–25^{\circ}C$ | Ensure chemical stability | Guarantees the anticoagulant functions as intended upon collection. |
Sourcing Quality EDTA Tubes
For procurement managers, ensuring you receive high-quality, long-dated stock is key. This means partnering with a reliable manufacturer who adheres to strict quality management standards.
Siny Medical Technology Co., Ltd has held ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 certifications since its establishment, ensuring every K3 EDTA Blood Collection Tubes and standard EDTA Tube meets stringent global benchmarks. We are committed to supplying products with optimal shelf life. You can review our quality standards and certifications.
Handling During Collection: Minimizing Pre-Analytic Error
Even with perfect storage, errors during the venipuncture and immediate post-collection phase can ruin a sample. Proper collection technique is inseparable from tube handling.
The Correct Order of Draw
One of the most critical handling procedures is adhering to the established order of draw. While EDTA Blood Collection Tubes are generally drawn late in the sequence (usually third or fourth, after sterile collection and serum tubes), it is essential to prevent cross-contamination.
If the tube is drawn too early, the EDTA anticoagulant can be carried over into subsequent non-additive or coagulation tubes. EDTA binds to calcium, which is essential for coagulation.9 Contamination can render a coagulation test invalid
Important Reminder: The EDTA Tube is part of a complex process. For a full protocol, review where the EDTA tube collection order fits in phlebotomy protocol.
Proper Mixing Technique
The EDTA additive must be thoroughly and gently mixed with the blood sample immediately after the tube is filled.10 This is perhaps the single most important step in tube handling post-collection.
- Why Mix? EDTA is either coated on the inner wall (as a liquid spray-dried additive) or present as a fine powder.11 It must dissolve and fully mix with the blood to prevent clotting. Clotting is the number one reason for rejection of an EDTA Blood Collection Tubes sample.
- How to Mix: Invert the tube gently 8 to 10 times. The inversion must be a complete $180^{\circ}$ turn.
- Avoid Shaking: Vigorous shaking or vortexing can cause hemolysis, which is the rupture of red blood cells.12 Hemolysis affects the CBC parameters and can also contaminate the plasma, making the sample unusable for certain chemistry tests. The inversion must be gentle enough to mix the contents without damaging the cells.
Ensuring Correct Volume Draw (Fill Line)
The blood-to-anticoagulant ratio is fixed and crucial. Every EDTA Tube has a designated fill volume, often indicated by a line or shoulder on the tube.13
- Underfilling: As noted, this is the most common issue. Too little blood means an excess of anticoagulant.14 This excess EDTA can cause red blood cells to shrink (crenation), invalidating cell volume measurements like Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV).15
- Overfilling: While less common with vacuum tubes, overfilling can dilute the anticoagulant, leading to micro-clot formation within the tube.16
- Correct Fill: Always use the correct volume tube for the intended test and allow the vacuum to draw the blood until flow stops completely.
Need specific sizes? We offer a full range of EDTA tube size options, including different volumes of our purple top blood collection tube.17 Check our available products.
K2 EDTA vs. K3 EDTA Tube: Understanding the Differences
Decision-makers in laboratory procurement often face the choice between K2 EDTA and K3 EDTA Tube. While both are highly effective anticoagulants (the “K” stands for potassium, which makes the EDTA soluble in blood), there are subtle differences recognized by global standards bodies.19
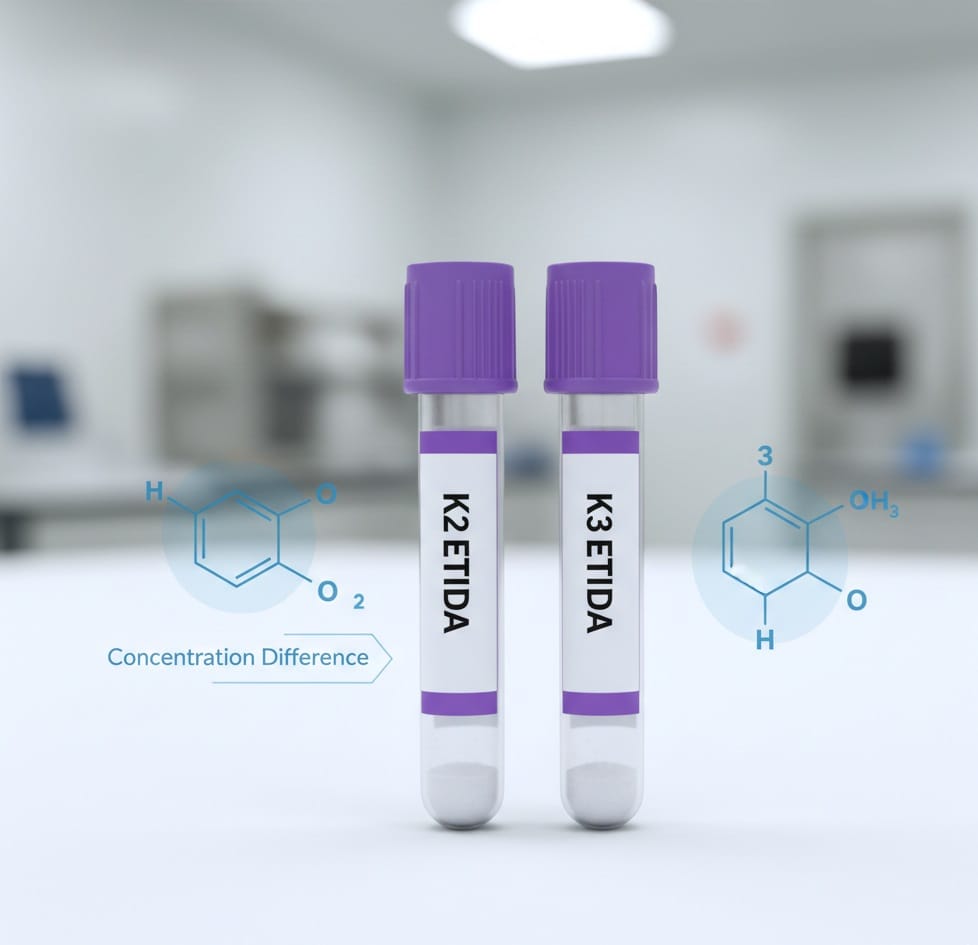

The Technical Distinction
Both are effective for routine hematology tests, but the differences lie in their concentration and impact on certain cell parameters.
| Feature | K2 EDTA | K3 EDTA Tube |
| Additive Form | Di-potassium salt | Tri-potassium salt |
| Volume Concentration | Typically added as $5.4 of blood | Typically added as $7.5 of blood |
| Effect on Cell Volume (MCV) | Minimal impact, considered more inert | Can cause a slight (1–2%) decrease in cell volume (MCV) if stored for extended periods. |
| Global Preference | Preferred by CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) | Widely used globally, especially in Europe and Asia |
| Trace Metal Interference | Less dilution effect | Slightly higher dilution (approx. $1–2\%$) due to greater additive volume. |
Procurement and Clinical Choice
For most routine Complete Blood Counts (CBCs) and blood typing, either K2 EDTA or K3 EDTA will yield reliable, high-quality results when used correctly.
- K2 EDTA: Often preferred by large reference labs in North America due to CLSI guidelines that cite its minimal effect on red blood cell volume.
- K3 EDTA Tube: Highly effective and cost-efficient. Many high-volume labs globally prefer this option, finding the slight volume change to be negligible in a well-managed laboratory setting.
Choosing the right tube means assessing your lab’s specific analyzer and protocol. We manufacture both and can provide detailed specifications for both our EDTA K2 and EDTA K3 vacuum blood collection tubes to help you make the best choice.
Considering EDTA Syringe Use and Transfer
While vacuum tubes are the standard for high-volume collection, sometimes a blood sample is collected via an EDTA syringe (e.g., from an indwelling line). In these cases, the sample must be transferred into an EDTA Blood Collection Tube.
- Never Push: Do not push the syringe plunger to force blood into the tube.20 This can cause high pressure and lead to severe hemolysis.
- Open and Pour: Remove the stopper and gently pour or allow the blood to drip from the syringe into the tube, taking care to fill to the designated line. The best practice is still to use a sterile transfer device if possible.
Transport and Post-Analytic Handling: Maintaining Sample Integrity
The sample’s life doesn’t end when the blood is drawn and mixed. Transporting the sample from the collection point to the analyzer is a crucial step that, if mishandled, can undo all the previous care.
Transportation Requirements
Blood drawn into EDTA Blood Collection Tubes is primarily used for hematology tests, which are sensitive to time and temperature.
- Time is Critical: For routine CBCs, the sample should ideally be analyzed within 6 to 8 hours of collection. After 24 hours at room temperature, significant changes in morphology (cell size and shape) and platelet count can occur. If testing is delayed beyond $24$ hours, refrigeration may be necessary, but this requires specific protocol knowledge as cold can also affect certain cells.
- Keep it Upright: Tubes should be transported and stored in a rack in an upright position.21 This prevents the blood from touching the stopper, which reduces the chance of contamination or leakage.
- Safety First: Transport in leak-proof, secondary containers that meet all biohazard safety regulations. Our EDTA Tubes are designed to be used with standard transport racks and pneumatic tube systems.
Handling Post-Testing
After the initial test, the tube is not always discarded immediately.
- Retention Policy: Most labs retain EDTA Blood Collection Tubes samples for 24 to 72 hours post-testing. This allows for re-runs, reflex testing, or add-on tests without requiring a new draw.
- Refrigeration: Retained samples are typically refrigerated ($2^{\circ}C$ to $8^{\circ}C$). It is important to label and organize these retained samples using the FIFO method (retire the oldest first).
- Re-mixing: If a refrigerated sample needs to be re-tested, it must be gently inverted (mixed) again before analysis to re-suspend any settled cellular components.
What is the EDTA Tube Used For Which Test?
Understanding the purpose of the tube reinforces the need for best practices. EDTA Tubes are essential for:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Differential White Blood Cell Count (Diff)
- Platelet Count
- Reticulocyte Count
- Blood Grouping/Typing (ABO/Rh)
- Crossmatching
- Flow Cytometry
- Sickle Cell Screening
The range of essential tests performed using blood from an EDTA Blood Collection Tube highlights why sample integrity is paramount—it affects fundamental diagnostic information.
Quality Assurance and Procurement: Your Partner in Diagnostics
For directors, procurement managers, and wholesale buyers, the discussion of handling and storage ultimately comes back to sourcing quality products. Best practices in handling can only succeed if the product itself is reliable.
Our factory, covering an area of $12,000$ square meters, is dedicated to producing high-end medical consumables. When you buy EDTA Blood Collection Tubes from Siny Medical, you are partnering with an original manufacturer established in 2003 with a global reputation for quality.
We encourage you to review our full range of products, including our EDTA Tubes for blood collection and our top-quality K3 EDTA Blood Collection Tubes.
Ready to streamline your lab’s inventory with a trusted, certified manufacturer? Contact us today to discuss wholesale orders and customized solutions. We are here to support your mission of delivering accurate diagnostics with ease.
Contact Us for Pricing and Wholesale Inquiries
Final Call to Action (CTA)
Stop worrying about your supply chain and focus on diagnostics. When you choose Siny Medical, you are choosing a manufacturer that has been delivering quality since 2003. We offer superior-grade K3 EDTA Blood Collection Tubes and other EDTA Tubes that adhere to the highest global certifications.
Don’t settle for less than the best. Take control of your sample quality by partnering with an original manufacturer who prioritizes accuracy and reliability.
Contact our sales team today for a direct quote on your next wholesale order. We are ready to be your trusted global supplier.
Get a Quote and Discuss Customization.
FAQs
Q1: What is the recommended storage temperature range for large-volume inventory of EDTA Tubes?
For procurement and logistics planning, you should maintain bulk inventory of EDTA Tubes at standard room temperature, specifically between. Storing within this range ensures the integrity of the vacuum seal and the stability of the K2 or K3 EDTA Tube anticoagulant, minimizing the risk of pre-analytic failure once the product is distributed to collection points.
Q2: Is there a significant clinical difference between using a K2 EDTA and a K3 EDTA Tube for routine CBC analysis?
From a clinical diagnostic perspective, the difference is minimal for routine analysis, especially if samples are analyzed within 6 hours. However, the CLSI recommends K2 EDTA because the K3 EDTA Tube contains a higher concentration of fluid additive, which can cause a negligible 1–2% dilution of the sample and a slight decrease in Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) over 24 hours. Buyers should select based on their specific analyzer validation and laboratory protocol; Siny Medical supplies both to meet global standards.
Q3: How do I ensure I am receiving competitive edta blood collection tubes price without compromising quality?
To secure the best edta blood collection tubes price while ensuring consistent quality, we recommend sourcing directly from a certified, established manufacturer like Siny Medical. By working with us, you cut out intermediary costs and benefit from our $12,000$ square meter factory’s efficiencies and adherence to ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 standards. This direct-from-manufacturer relationship guarantees you both value and the high-end product quality your lab requires.
We are a wholesale distributor; can Siny Medical customize EDTA Tube labeling and packaging for us?
Yes. As a scientific and technological enterprise integrating R&D, production, and sales since 2003, customization is one of our core strengths. We offer private labeling, customized packaging, and the flexibility to meet specific volume and size requirements for your EDTA Tubes. Please contact us to discuss your specific branding and logistics needs for edta blood collection tubes for sale.