In clinical laboratories, precision isn’t just important—it’s everything. A single inaccurate result can alter a diagnosis, affect patient treatment, or even endanger lives. That’s why maintaining the integrity of blood samples from the moment of collection is a top priority.
Among the various blood collection systems, EDTA tubes have become the universal standard, particularly for hematology testing. But what makes them so effective? How do they ensure blood remains unclotted and suitable for testing even hours after collection?
Let’s dive deep into the science and technology behind how EDTA tubes prevent blood from clotting and why every healthcare professional should understand their role.
The Science Behind EDTA Tubes
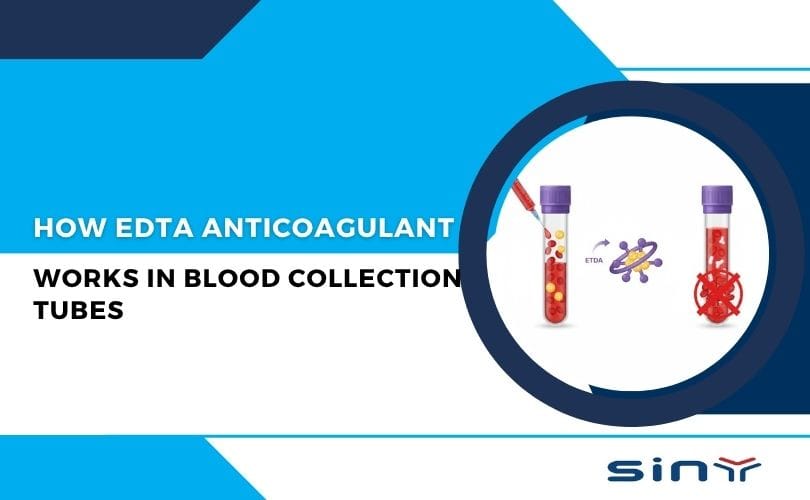
At the heart of every EDTA tube lies its key ingredient — Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), a powerful chelating agent. This compound’s unique ability to bind with calcium ions (Ca²⁺) forms the foundation of its anticoagulant properties.

Here’s how it works:
The blood clotting cascade relies on calcium ions to activate enzymes that trigger clot formation.
When blood enters an EDTA-coated tube, the EDTA binds with calcium almost instantly, creating a stable complex.
Without free calcium, the clotting cascade halts, and the blood remains fluid for analysis.
This simple but effective reaction ensures that EDTA tubes prevent blood from clotting, keeping samples viable for tests like Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR).
Beyond just anticoagulation, EDTA preserves cell morphology—the natural shape and size of red blood cells, white cells, and platelets—ensuring accurate microscopic and automated counts.
For in-depth product specifications, check out EDTA Tubes for Blood Collection.
Why Tube Quality Matters in Diagnostics
The accuracy of any blood test depends not only on laboratory expertise but also on the quality of the consumables used. A poorly manufactured EDTA tube can lead to clotting, inaccurate readings, or even damage to blood cells—all of which can compromise results and patient care.
Here’s what defines a high-quality EDTA tube:
- Proper EDTA Coating: The anticoagulant must be evenly and precisely applied inside the tube. Too little can cause microclots; too much can affect cell structure. Advanced manufacturers use spray-drying technology to ensure uniform coverage.
- Reliable Sterility and Material Safety: Medical-grade PET or glass tubes are preferred to prevent breakage and contamination.
- Correct Vacuum Calibration: The vacuum level determines the right blood-to-additive ratio, ensuring accurate laboratory measurements.
- Clear Labeling and Color-Coding: The lavender or purple cap makes EDTA tubes instantly recognizable, minimizing the risk of mix-ups in busy labs.
Using substandard tubes can lead to misdiagnosis, repeated testing, and wasted resources. For healthcare providers and distributors alike, investing in dependable EDTA tubes means investing in trust, efficiency, and patient safety.
For a deeper dive into QC procedures, read Top Quality Control Tips for Using EDTA Tubes.
Using poor-quality tubes leads to wasted time, repeated tests, and unreliable diagnostics. In healthcare, quality equals trust—a standard upheld by reputable brands like Siny Medical.
Choosing the Right Supplier
In a crowded market, selecting a supplier for medical consumables can be challenging. While price is often a tempting factor, in healthcare, reliability always outweighs short-term savings.
A reputable EDTA tube supplier should demonstrate:
- Certification and Quality Standards: Look for ISO 13485 or equivalent certifications that prove consistent production quality.
- Advanced Manufacturing and QC: Automation and rigorous quality control at every stage ensure consistent performance.
- Traceability and Support: Reliable suppliers offer batch traceability, technical support, and complete documentation for every product.
- Proven Industry Reputation: Choose a supplier with long-term experience and positive customer feedback in the medical consumables field.
Selecting the right partner ensures that every EDTA tube you use performs as expected—reducing errors, ensuring consistency, and building confidence in your diagnostic services. To explore high-quality EDTA tube solutions, visit edtatube.com.
The Role of EDTA in Preserving Blood Cell Integrity
EDTA doesn’t just prevent clotting; it preserves blood cell morphology over time. This makes it indispensable in hematology and molecular diagnostics.
Here’s why:
EDTA keeps red and white blood cells intact, preventing swelling or lysis.
It stabilizes platelets, allowing accurate platelet counts.
It maintains sample stability for DNA and RNA analysis, preventing degradation.
Other anticoagulants like heparin or sodium citrate may alter cell size or cause aggregation if samples aren’t processed quickly. That’s why EDTA remains the anticoagulant of choice worldwide for hematology.
Learn how to properly handle and store these samples at How to Use an EDTA Tube.
K₂EDTA vs. K₃EDTA: Understanding the Difference
Not all EDTA tubes are created equal. The difference between K₂EDTA and K₃EDTA lies in their chemical form and how they interact with blood.
| Property | K₂EDTA (Dipotassium EDTA) | K₃EDTA (Tripotassium EDTA) |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Spray-dried (powdered) | Liquid additive |
| Dilution Effect | None (no dilution) | Slight dilution |
| Recommended By | International Council for Standardization in Hematology (ICSH) | Used in limited tests |
| Cell Morphology | Better preservation | May cause slight shrinkage |
| Best For | CBC, differential counts, hematology | ESR, specific assays |
K₂EDTA is generally preferred due to its stability and non-dilutive nature. It minimizes cellular distortion and maintains accurate hematological parameters, even when analysis is delayed.
Explore both types in detail at EDTA K2 & K3 Whole Blood Tubes.
The Chemistry Behind Calcium Chelation
To fully understand how EDTA tubes prevent blood from clotting, it helps to explore the chemical process:
EDTA contains four carboxylic acid groups and two amine groups capable of chelating divalent cations, especially Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺. When EDTA binds calcium, it forms a stable hexadentate complex, making calcium unavailable for coagulation reactions.
This reaction effectively halts key enzymatic pathways—like thrombin activation and fibrin formation—which are essential for clot development.
For those interested in the molecular structure and reaction pathways, you can find detailed videos on the Siny Medical YouTube Channel.
Importance of Correct Blood-to-EDTA Ratio
Even though EDTA is highly effective, its concentration must be precise. Too little EDTA can result in microclots; too much can alter cell morphology.
Most manufacturers calibrate tubes to maintain an EDTA concentration of 1.5–2.2 mg per mL of blood, which ensures optimal anticoagulation without cellular interference.
Vacuum calibration is another key factor — improper pressure can affect the blood draw volume and distort the blood-to-additive ratio. That’s why tubes from EDTA Tube are meticulously tested to ensure accuracy.
How to Choose the Right EDTA Tube for Your Lab
Choosing the right tube type depends on your test requirements, analyzer compatibility, and storage needs.
Consider these factors:
Tube Volume and Size: Select appropriate volumes (2 mL, 3 mL, 5 mL, etc.) for adult or pediatric samples.
Closure Type: Safety caps reduce aerosol contamination.
Additive Type: K₂EDTA for hematology, K₃EDTA for ESR.
Material: PET plastic offers lightweight safety compared to glass.
To explore the full range, visit How to Choose the Right EDTA Tube for Your Lab.
Handling and Storage: Best Practices
Proper handling is just as important as tube selection.
Gently invert the tube 8–10 times after collection to mix blood with EDTA evenly.
Avoid shaking — it can cause hemolysis.
Store at 2–8°C if testing is delayed beyond 6 hours.
Never freeze EDTA blood samples.
Incorrect handling can compromise the sample and cause inaccurate results.
Learn more about handling techniques at EDTA Separation Gel & Coagulation Tubes.
Quality and Certification: Why Trust Matters
In medical diagnostics, trust comes from certification and consistency. Always select tubes that meet ISO 13485 and CE certification standards.
Reputable suppliers like EDTA Tube and Siny Medical ensure every batch is traceable and quality-checked before distribution.
With automated production lines and sterile packaging, they deliver superior performance across hospitals, research centers, and diagnostic labs worldwide.
Final Thoughts
EDTA tubes are small yet vital components of modern diagnostics. Their ability to preserve blood samples accurately underpins the reliability of countless medical tests. By understanding how they work—and by choosing trusted, certified products—healthcare professionals can uphold the highest standards of diagnostic precision.
For clinics, laboratories, and distributors seeking dependable EDTA tubes, edtatube.com offers solutions built on quality, consistency, and scientific integrity. Explore our range of products, including EDTA tubes for blood collection and EDTA K2/K3 tubes, to ensure your diagnostic processes are as accurate and reliable as possible. For more insights, check out our guide on how to choose the right EDTA tube for your lab.
FAQs
Q1: What is the main function of an EDTA tube?
EDTA binds calcium ions, preventing the coagulation cascade from starting. It’s ideal for hematological analyses like CBC and ESR tests.
Q2: Why should the EDTA tube be inverted after blood collection?
Gently inverting the tube 8–10 times ensures proper mixing of blood and anticoagulant, preventing microclot formation.
Q3: What’s the difference between K₂EDTA and K₃EDTA tubes?
K₂EDTA is spray-dried and non-dilutive; K₃EDTA is liquid-based and may slightly alter cell size.
Q4: Can EDTA tubes be used for all blood tests?
No. Avoid using EDTA tubes for biochemical assays measuring calcium, magnesium, or clotting-related enzymes.
Q5: How does tube quality affect test accuracy?
Poor-quality tubes can lead to clotting or cell lysis. Certified tubes ensure consistent, accurate, and reproducible results.