EDTA tubes are specialized blood collection containers that play a crucial role in modern medical diagnostics. Their primary function is to prevent EDTA Tubes Blood Clotting, ensuring the integrity of blood samples for accurate laboratory analysis. This document will explore the composition, mechanism of action, applications, and advantages of EDTA tubes, as well as their significance in various medical fields.
What is EDTA?
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is a chelating agent that binds to metal ions, particularly calcium, which is essential for the blood coagulation process. By sequestering calcium ions, EDTA effectively inhibits the cascade of reactions that lead to clot formation. This property makes EDTA an ideal anticoagulant for blood samples intended for hematological tests and other diagnostic procedures.
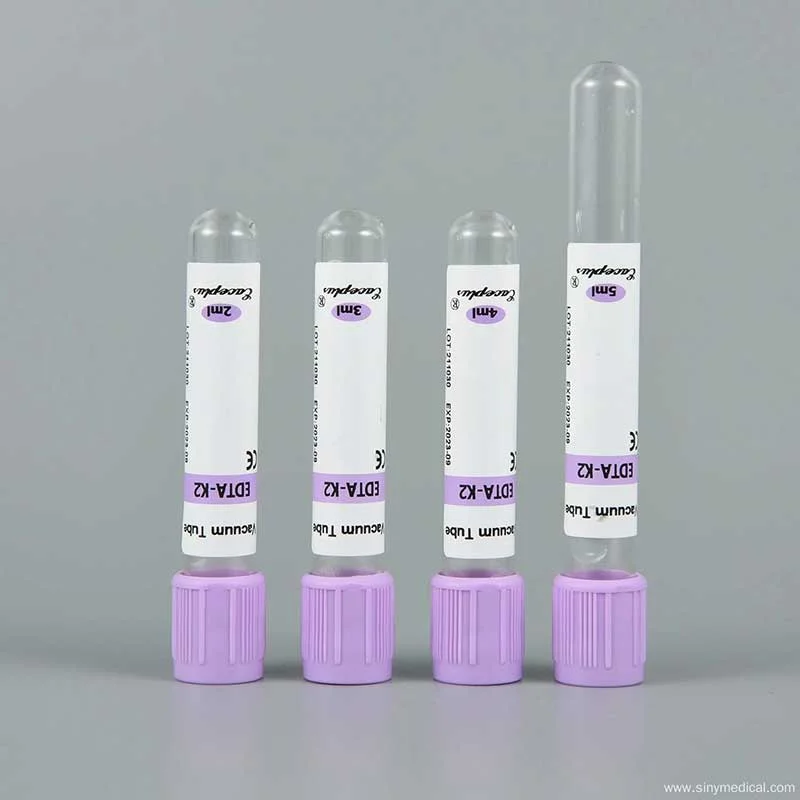
Composition of EDTA Tubes
EDTA Tubes Blood Clotting typically contain:
EDTA: The active anticoagulant agent, available in two forms:
- K2 EDTA: Contains two potassium ions.
- K3 EDTA: Contains three potassium ions.
Sterile Environment: Ensures that the blood sample remains uncontaminated during collection and transport.
Color-Coded Caps: Different colors indicate the type of anticoagulant used and help in quick identification during laboratory processes.
Role of EDTA in Blood Collection and Preservation
When blood is collected in an EDTA tube, the anticoagulant works immediately to prevent clotting. This is particularly important in tests such as Complete Blood Count (CBC), where the shape, number, and type of blood cells must be preserved for analysis. Clotting would alter the shape of red blood cells, leading to inaccurate readings of cell morphology, which is essential in diagnosing conditions like anemia or leukemia.
EDTA’s ability to preserve blood cells also ensures that white blood cells and platelets are not affected during the analysis. In tests that require an analysis of these cells, such as those for diagnosing infections or monitoring platelet function, EDTA ensures that the cells remain viable for the duration of the analysis.
EDTA Tubes in Clinical Diagnostics
EDTA tubes are predominantly used for hematology tests, as they prevent clotting while preserving the structure and integrity of blood cells. Here are some common applications of EDTA tubes in clinical diagnostics:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This is one of the most commonly requested blood tests, and EDTA tubes are the standard for collecting samples. The CBC provides information on the number and types of blood cells, which can help diagnose conditions like anemia, infections, and blood cancers.
- Blood Typing and Cross-Matching: EDTA tubes are used for blood typing and cross-matching, ensuring that blood transfusions are safe and that the patient receives compatible blood.
- Platelet Function Testing: Since EDTA prevents clotting, it is ideal for testing platelet function in diagnosing disorders such as thrombocytopathy, where platelets do not function properly.
- Infectious Disease Testing: EDTA tubes are used in testing for various infectious diseases, such as malaria or HIV, where it is crucial to analyze the blood’s cellular components.
- Flow Cytometry: EDTA tubes are used in flow cytometry, a technique used to examine the characteristics of cells, particularly for research and diagnosis of cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Advantages and Limitations of EDTA Tubes Blood Clotting
Advantages:
- Prevention of Clotting: EDTA is highly effective at preventing blood clotting, ensuring accurate analysis of blood cells.
- Preservation of Cell Integrity: EDTA tubes help preserve the morphology and viability of blood cells, which is crucial for accurate test results.
- Compatibility with Various Tests: EDTA tubes are ideal for a wide range of hematology tests, including CBC and blood typing.
Limitations:
- Effect on Coagulation Tests: EDTA is not suitable for tests that measure blood clotting, such as prothrombin time (PT) or activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), as it interferes with these tests by preventing clot formation.
- Platelet Clumping: In some cases, EDTA can cause platelet clumping, leading to inaccurate platelet count results.
- Short-Term Storage: While EDTA tubes are suitable for short-term storage, long-term storage of blood samples in EDTA tubes may lead to alterations in blood cell morphology.
Comparison with Other Anticoagulants
While there are several anticoagulants available for blood collection, such as citrate and heparin, EDTA offers unique benefits:
| Anticoagulant | Mechanism | Best Use Cases | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | Binds calcium | Hematology tests | Not suitable for coagulation studies |
| Citrate | Binds calcium | Coagulation studies | Requires recalibration for some tests |
| Heparin | Inhibits thrombin | Biochemistry tests | Can interfere with some assays |
Conclusion
EDTA tubes are vital in the field of laboratory medicine, particularly for tests requiring the analysis of blood components without the interference of clotting. Their ability to chelate calcium ions effectively prevents coagulation, ensuring that blood samples remain suitable for accurate testing. Understanding the role of EDTA tubes product in blood collection is essential for healthcare professionals involved in diagnostic processes.
FAQs
What is the role of EDTA in blood clotting?
EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is an anticoagulant that plays a crucial role in preventing blood clotting. It does this by chelating or binding to calcium ions in the blood. Calcium is a vital component in the clotting cascade, as it is required for several steps in the process of EDTA tube for blood collections.
What is the purpose of the EDTA blood tube?
The primary purpose of an EDTA blood tube is to collect blood samples while preventing coagulation, ensuring that the blood stays in its liquid form during transport and analysis. EDTA is the anticoagulant used in these tubes because it effectively binds calcium ions, which are essential for blood clotting. This allows accurate measurement and analysis of blood components, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin, which are all critical in tests like a Complete Blood Count (CBC).
How does EDTA prevent blood clotting by binding?
EDTA prevents blood clotting by binding to calcium ions in the blood. Calcium ions are critical to the clotting process because they activate several clotting factors (proteins involved in coagulation). When blood vessels are injured, a series of chemical reactions, known as the clotting cascade, occurs, which requires calcium to form a clot and stop bleeding. By binding to calcium ions, EDTA “chelates” them and removes them from the bloodstream.
Can EDTA tubes be used for serum tests?
No, EDTA tubes are not used for serum tests. Serum is obtained from blood that has been allowed to clot, and EDTA tubes prevent clotting. For serum tests, such as those measuring blood glucose or cholesterol, plain tubes or those containing clot activators are used.
What is the difference between K2 and K3 EDTA?
The main difference between K2 and K3 EDTA lies in their form. K2 EDTA is a powder that needs to dissolve when blood is collected, while K3 EDTA is already in a liquid form. Both types serve the same function of preventing blood clotting, but K2 is more commonly used in vacuum-sealed tubes.