The color of the tube cap plays a crucial role in identifying the type of additive used and the purpose of the tube. One of the most commonly used tubes in medical laboratories is the EDTA tube, known for its distinct color coding. But what color top does an EDTA tube have? In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the specifics of EDTA tubes, their purpose, and why their color coding is essential for accurate diagnostics.
What is an EDTA Tube?
EDTA tubes are specialized blood collection tubes that contain ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as an anticoagulant. EDTA prevents blood clotting by binding to calcium ions, ensuring that the blood sample remains in its liquid state for various laboratory tests. These tubes are widely used for complete blood count (CBC), blood typing, and other hematological analyses.
To learn more about what EDTA tubes are and how they work, visit our detailed guide here.
The Color Code of EDTA Tubes
The most distinctive feature of an EDTA tube is its purple or lavender top. This color coding is standardized globally to ensure consistency in blood collection practices. The purple top indicates that the tube contains K2 EDTA or K3 EDTA, which are the most common forms of EDTA used in blood collection.
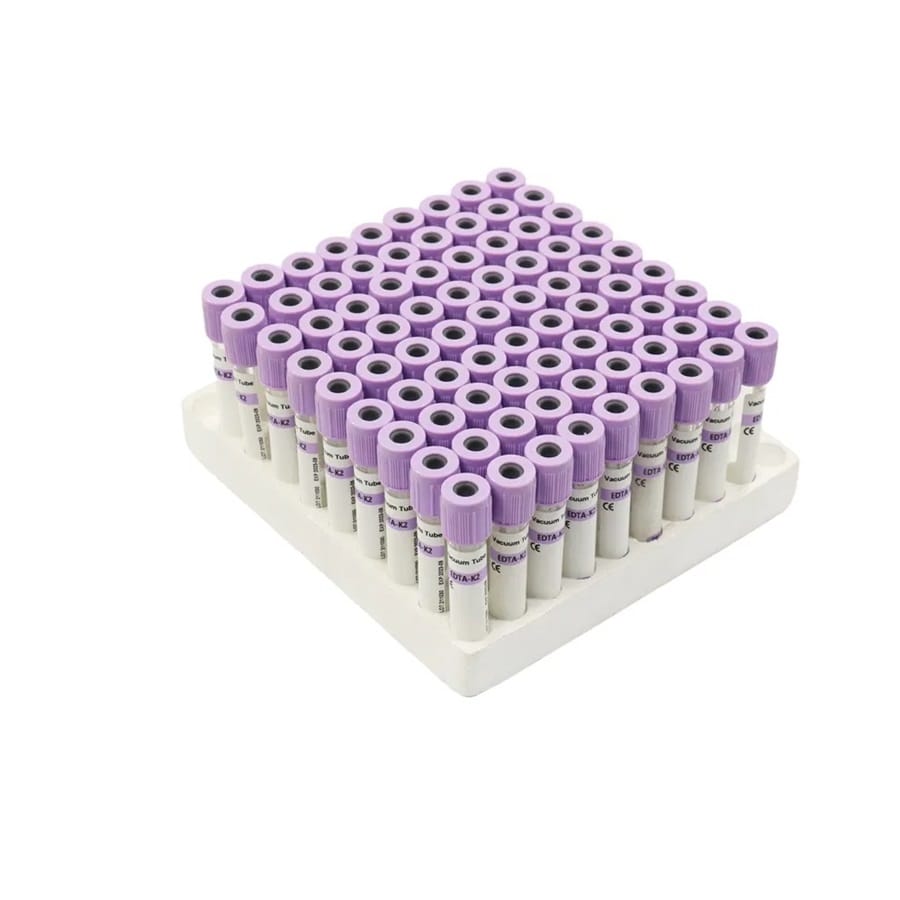

For a closer look at the purple-top EDTA tubes, check out our product page here.
Why is the Purple Top Important?
The purple top serves as a visual cue for healthcare professionals, ensuring that the correct tube is used for specific tests. Using the wrong tube can lead to inaccurate results, affecting patient diagnosis and treatment. For example, using a tube without EDTA for a CBC test could result in clotting, rendering the sample unusable.
To understand how EDTA in purple-top tubes works, read our article here.
Types of EDTA Tubes
While the purple top is the most common, EDTA tubes can come in different forms depending on the specific application:
- Lavender Top: Contains K2 EDTA and is used for most hematological tests.
- Pink Top: Contains K2 EDTA and is often used for blood bank procedures.
- White Top: Contains K2 EDTA and is used for molecular diagnostics.
Explore our wide range of EDTA tubes here.
How Does EDTA Work in Purple Top Tubes?
The science behind it is fascinating. EDTA binds calcium, and since calcium is vital for clotting, the absence of free calcium prevents clots from forming. This means blood cells stay suspended, maintaining their original size, shape, and structure.
Hematology – EDTA preserves red and white cells for accurate counts.
Molecular Biology – EDTA tubes safeguard DNA and RNA for genetic testing.
Transfusion Medicine – Prevents clotting during blood typing and cross-matching.
👉 Check out How EDTA in Purple Top Tubes Works for a technical deep dive.
Applications of EDTA Tubes
EDTA tubes are indispensable in various medical and laboratory settings. Some of their key applications include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To analyze red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Blood Typing: To determine blood group and Rh factor.
- Molecular Diagnostics: For DNA and RNA extraction.
- Immunology: For testing immune system function.
Discover more about the uses of EDTA tubes here.
Choosing the Right EDTA Tube
Selecting the appropriate EDTA tube depends on the type of test being performed. Factors to consider include:
- Additive Concentration: Ensure the correct amount of EDTA is used to avoid sample hemolysis.
- Tube Size: Choose the appropriate tube size based on the volume of blood required.
- Application: Select the tube type based on the specific diagnostic needs.
For expert guidance on choosing the right EDTA tube, visit Sinymedical.
Tips for Proper Blood Collection with EDTA Tubes
To ensure accurate results, follow these best practices when using EDTA tubes:
- Fill the Tube Completely: Incomplete filling can lead to incorrect anticoagulant-to-blood ratios.
- Mix Gently: Invert the tube 8-10 times to ensure proper mixing of EDTA with the blood.
- Avoid Hemolysis: Handle the tube carefully to prevent red blood cell rupture.
- Label Correctly: Ensure the tube is properly labeled to avoid sample mix-ups.
Summary
The purple top of EDTA tubes is a universally recognized symbol in blood collection, ensuring that the correct anticoagulant is used for hematological tests. Understanding the purpose, types, and proper usage of EDTA tubes is essential for accurate diagnostics and patient care. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a laboratory technician, knowing the significance of the purple top can make a significant difference in your work.
For more information about EDTA tubes and their applications, visit our website here. If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to contact us.
FAQs
1. What color is an EDTA tube?
An EDTA tube has a purple (lavender) top.
2. Why is the EDTA tube purple?
The purple color is part of the international coding system to indicate EDTA as the anticoagulant.
3. What tests are done with EDTA tubes?
They’re mainly used for hematology tests like CBC, ESR, and blood film studies.
4. Can EDTA tubes be used for glucose testing?
No, glucose tests require gray-top fluoride tubes.
5. Where can I buy EDTA tubes?
You can purchase directly from EDTA Tube Official Website.