When researchers ask what does EDTA do in DNA extraction, they are really asking how DNA stays intact, stable, and usable during one of the most delicate laboratory processes. DNA extraction is not just about breaking cells open. It is about protecting genetic material from destruction at every step. This is where EDTA becomes indispensable.
EDTA, short for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, is a chelating agent that quietly performs one of the most critical jobs in molecular biology. Without it, DNA extraction would often result in fragmented, degraded samples unsuitable for PCR, sequencing, cloning, or diagnostic testing. From academic research labs to clinical diagnostics and biotechnology manufacturing, EDTA is a foundational component of reliable DNA isolation.
This in-depth guide explains what EDTA does in DNA extraction, how it works chemically, why it improves DNA quality, and how it connects directly to sample collection tools such as EDTA tubes. Along the way, we also discuss practical considerations for laboratories, procurement teams, and quality-focused professionals sourcing EDTA-based products from trusted suppliers like edtatube.
The Role of EDTA in DNA Extraction
To clearly understand what EDTA does in DNA extraction, it is essential to look at its chemical behavior. EDTA is widely used in molecular biology because it chelates divalent metal ions such as magnesium (Mg²⁺) and calcium (Ca²⁺), binding them tightly and preventing them from participating in other biochemical reactions.
These metal ions are required cofactors for nucleases — enzymes naturally present in cells that can rapidly degrade DNA once cellular structures are disrupted. By binding Mg²⁺ and Ca²⁺, EDTA effectively inhibits nuclease activity, protecting DNA from enzymatic degradation throughout the extraction process. As a result, DNA remains intact, stable, and suitable for downstream analysis.
Beyond nuclease inhibition, EDTA also contributes to buffer stability, helping maintain a controlled chemical environment during extraction. This stability is essential for preserving DNA quality and supporting later applications such as PCR, sequencing, and cloning.
Why DNA Is Vulnerable During Extraction
DNA extraction involves controlled destruction. Cell membranes, nuclear envelopes, and proteins are intentionally disrupted to release genetic material. However, once DNA is free, it becomes extremely vulnerable.
Mechanical stress, temperature changes, and enzymatic activity can rapidly break DNA strands. Even trace nuclease activity can reduce yield and compromise quality. This vulnerability explains why EDTA appears so consistently across DNA extraction protocols.
When scientists evaluate what EDTA does in DNA extraction, they are acknowledging its role as a molecular bodyguard. EDTA does not extract DNA itself. Instead, it ensures DNA survives the extraction process intact.
How EDTA Functions Throughout the DNA Extraction Workflow
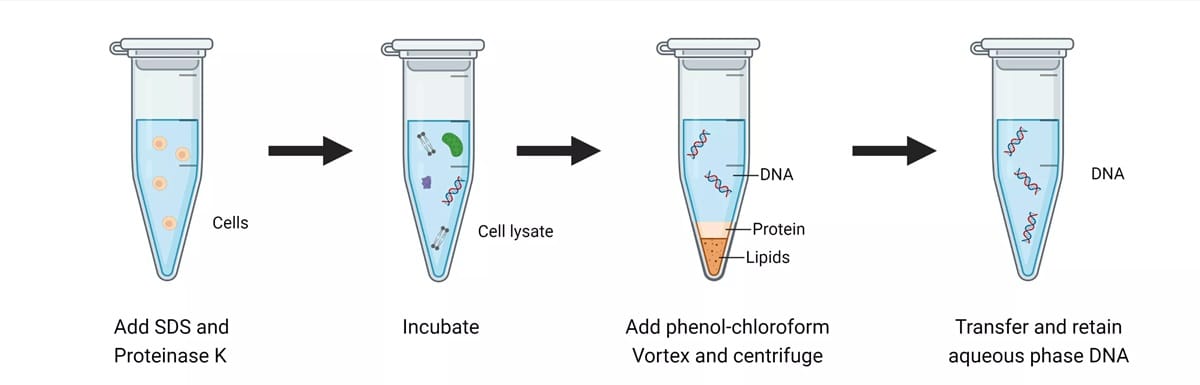
EDTA During Cell Lysis
During cell lysis, detergents and mechanical forces disrupt cellular membranes. EDTA assists by destabilizing membrane structures that rely on calcium ions for integrity. While EDTA is not a detergent, its ion-chelating action supports efficient lysis.
More importantly, EDTA begins protecting DNA immediately. The moment nucleases are released, EDTA starts inhibiting them.
EDTA and Nuclease Inhibition
This is the most critical answer to what does EDTA do in DNA extraction. Nucleases require Mg²⁺ or Ca²⁺ to function. EDTA sequesters these ions, rendering nucleases inactive.
Studies consistently show that DNA extracted without chelating agents is more prone to fragmentation. EDTA dramatically reduces this risk, leading to higher molecular weight DNA and improved downstream reliability.
Maintaining DNA Solubility
Metal ions can interact with the phosphate backbone of DNA, causing aggregation or precipitation under certain conditions. EDTA prevents these interactions by binding free ions. This keeps DNA soluble and easier to purify.
Uses of EDTA in DNA Extraction Protocols
After understanding what EDTA does in DNA extraction, it is useful to examine how it appears in common laboratory reagents and buffers.
Tris-EDTA (TE) Buffer
One of the most widely used applications is the TE buffer, which combines Tris for pH control with EDTA for nuclease inhibition. TE buffer is commonly used to resuspend purified DNA and protect it during storage or handling.
Lysis and Extraction Buffers
Many DNA extraction kits incorporate EDTA directly into their lysis formulations, where it helps prevent DNA degradation from the earliest stages of extraction.
Specialized Extraction Reagents
In advanced extraction methods, such as phenol-chloroform or magnetic bead-based protocols, EDTA is frequently included to maximize DNA integrity before purification and downstream analysis.
Because of these advantages, EDTA is considered a standard component in most molecular biology extraction systems.
Downstream Considerations — Balancing Protection and Compatibility
When evaluating the role of EDTA in DNA extraction, it is also important to consider its impact on downstream applications.
Protection Versus Enzyme Inhibition
While EDTA protects DNA during extraction, excessive EDTA can interfere with enzymatic reactions used later, such as PCR amplification, restriction digestion, or ligation. These reactions rely on metal ions, such as Mg²⁺, which EDTA can sequester if present at high concentrations.
To address this, extraction protocols are typically designed with optimized EDTA levels, and additional purification steps may be used to remove excess EDTA before downstream processing.
Optimizing Extraction for Intended Use
Careful control of EDTA concentration ensures that DNA remains protected during extraction without compromising later analytical performance. This balance is critical for laboratories performing sensitive molecular assays.
The Role of EDTA Blood Collection Tubes in DNA Extraction
EDTA’s influence begins even before DNA extraction starts. In clinical and research settings, blood samples are often collected in EDTA tubes. These tubes prevent clotting by chelating calcium and help preserve nucleic acids during storage and transport.
High-quality EDTA tubes ensure accurate additive concentration and uniform coating. Poor-quality tubes may introduce variability, leading to inconsistent DNA yield.
Laboratories sourcing EDTA tubes often review technical specifications, shelf-life data, and manufacturing standards. Resources such as EDTA blood collection tube expiration and shelf-life guides help buyers make informed decisions.
For an overview of available products, laboratories can explore EDTA tube product listings and EDTA tubes for blood collection.
Why Supplier Quality Matters for EDTA-Based Products
When evaluating what EDTA does in DNA extraction, product quality is often overlooked. EDTA concentration, tube material, sterility, and manufacturing consistency all influence outcomes.
Reputable manufacturers follow strict quality control processes to ensure EDTA purity and performance. This is why many laboratories review multiple suppliers and consult external references such as Siny Medical’s EDTA tube overview or manufacturing profiles on platforms like Made-in-China.
Educational resources, including laboratory demonstrations available through channels like Siny Medical on YouTube, also help professionals understand proper EDTA usage.
Final Summary
So, what does EDTA do in DNA extraction? It protects DNA at its most vulnerable moments. By chelating divalent metal ions, EDTA inhibits nucleases, stabilizes extraction buffers, maintains DNA solubility, and improves overall yield and quality.
At the same time, careful control of EDTA concentration ensures compatibility with downstream applications. When paired with high-quality consumables and reliable suppliers, EDTA becomes a cornerstone of reproducible molecular biology workflows.
For laboratories, researchers, and procurement teams, understanding what EDTA does in DNA extraction is not just theoretical knowledge. It directly influences results, efficiency, and confidence in every DNA-based analysis.
FAQs
Why is EDTA used in DNA extraction buffers?
EDTA binds metal ions required by nucleases, which explains what EDTA does in DNA extraction by preventing DNA degradation during processing.
Can EDTA interfere with PCR or sequencing?
Yes, residual EDTA can inhibit enzymes. This is why protocols remove excess EDTA after extraction while still benefiting from what EDTA does in DNA extraction.
Is EDTA required for all DNA extraction methods?
Not strictly, but most methods include it because what EDTA does in DNA extraction significantly improves DNA integrity and yield.
Does EDTA improve DNA yield or just quality?
It improves both. By preventing degradation and aggregation, what EDTA does in DNA extraction helps preserve more intact DNA.
Do EDTA tubes matter before DNA extraction?
Absolutely. High-quality EDTA tubes support what EDTA does in DNA extraction by preserving nucleic acids from the moment of collection.